The best countries to register a small business
The evolution of technology is transforming conventional business procedures, engendering novel opportunities and trials for enterprises. In the epoch of heightened globalization, markets are becoming increasingly intertwined, necessitating that firms acclimate to evolving international norms and stipulations. These elements wield a profound influence on the determination of where to establish a small enterprise, as well as on protracted strategic resolutions. In this treatise, we shall examine how precisely these tendencies affect the choice of which nation to incorporate a small business.
Globalization of markets and its impact on choosing a jurisdiction for registering a small business
In an epoch of globalized economies and technological metamorphoses, selecting a jurisdiction for the establishment of petite enterprises assumes paramount significance. Whereas erstwhile diminutive ventures concentrated on provincial markets, contemporary entrepreneurs are vigorously probing international arenas to augment their clientele, amplify revenues, and refine expenditures.
Transnational rivalry, technological evolution, and the diminution of trade impediments have engendered prospects for modest enterprises that were erstwhile accessible solely to large conglomerates. Concurrent with these prospects, globalization also begets tribulations. In selecting a locale for registering a modest enterprise, one must heed both the attributes of one's nation and global economic phenomena, alterations in international jurisprudence, prevailing fiscal regulations, and transnational trade stipulations. Another pivotal consideration may be the availability of distinctive conditions for enticing international capital, preferential fiscal regimes, customs concessions, and the potentiality for unimpeded capital export.
Another crucial facet of globalization is ingress to global markets via commercial accords. For instance, the registration of minor enterprises within the European Union permits ingress to the unified European marketplace, which significantly facilitates commerce within the territory. Concurrently, nations such as Singapore and Hong Kong offer the prospect to engage with expansive Asian markets that are evolving at a brisk tempo.
Contemporary innovations assume a pivotal role in commerce and frequently dictate its competitiveness. Digitalization, mechanization, and the deployment of artificial intelligence can markedly diminish operational expenditures and amplify process efficacy, which engenders alterations in priorities when selecting a jurisdiction to inaugurate a modest enterprise.
The dependability and lucidity of the jurisprudential framework is another crucial facet. Entrepreneurs incline towards establishing their enterprises in nations with foreseeable legal apparatuses, where statutes are distinctly articulated and upheld at every stratum, and robust safeguarding of intellectual property and agreements.
Advantages of choosing a foreign jurisdiction for small businesses
Minor enterprises are the dynamo of the economy, engendering employment, ingenuity, and contributing to the augmentation of national revenue. Selecting a locus to establish a firm profoundly influences its triumph, lucrativeness, and capacity to vie.
One of the palpable advantages of enlisting a diminutive enterprise overseas are fiscal advantages. Administrations across the globe are instituting fiscal reforms designed to alleviate the fiscal encumbrance on modest enterprises, proffering inducements and streamlined fiscal schemas, which permits such firms to flourish and sustain their competitiveness.
A plethora of jurisdictions employ a fiscal schema wherein diminutive enterprises are encumbered with diminished tax levies relative to colossal conglomerates. This is executed with the objective of conferring supplementary advantages and galvanizing the expansion of petite firms, thereby guaranteeing their viability and endurance in the marketplace. Specifically, this liberates assets for subsequent augmentation and investment.
An exemplar is the reformation in the United States, wherein in 2017 the levies on petite enterprises were mitigated under the aegis of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. The reformation diminished the corporate levy from 35% to 21%, and also instituted an abatement of 20% of revenue for diminutive business proprietors, which markedly alleviated the fiscal encumbrance on venture creators.
Another facet of tax reformation is the diminution of bureaucratic impediments and the streamlining of protocols. Streamlined documentation schemas and the capability to tender tax declarations electronically mitigate temporal and pecuniary expenditures. Incorporation of enterprises in extrinsic jurisdictions may confer the prerogative to avail oneself of tax amnesties during the nascent phase of evolution. Such advantages may encompass exemption from revenue levies, abatement of VAT, or other fiscal duties.
In addition to direct levies, numerous nations are instituting fiscal inducements for specific pursuits, such as inquiry and ingenuity, as well as technological and monetary sectors. The digitization of fiscal mechanisms is one of the pivotal facets of contemporary tax overhauls. The shift to digital submissions, mechanization of tax scrutiny procedures, and the adoption of blockchain innovations can substantially alleviate the fiscal encumbrance on petite enterprises.
The next benefit that can provide business registration in a foreign jurisdiction, - reliable asset protection. As cross-border business transactions become increasingly complex, choosing a jurisdiction with a strong legal system can make all the difference when it comes to small business registration. Such jurisdictions take a strategic approach to managing and protecting personal and corporate assets from potential risks such as lawsuits and financial crises. Many jurisdictions offer legal structures that provide their owners with limited liability. Other jurisdictions provide the ability to create trusts and foundations, which allow assets to be transferred into special legal structures, providing an additional layer of protection against claims and lawsuits.
Opening a small business abroad in those states where laws clearly regulate property rights and courts effectively protect business interests, reduce risks and increase the chances of long-term success. Countries with developed legal systems offer clear and efficient procedures for resolving commercial disputes, which minimizes losses and time spent on litigation. An example of countries with a strong legal system is Singapore, which offers a high degree of legal protection and independent judicial processes, and is a reliable center for resolving international disputes, including through alternative methods such as arbitration or mediation.
Registering a business in another country may be beneficial due toforgiven regulatory requirements, which reduces administrative costs for businesses. This may include simplified reporting procedures, no requirement for a physical office presence, etc. Some countries offer flexibility regarding inspections and audits, which reduces the bureaucratic burden on businesses.
Such jurisdictions furnish digital instruments for registering and executing commercial activities (e.g. BizFile+ in Singapore), enabling the establishment of a company, submission of annual reports, and remittance of taxes through a single platform. This is advantageous for diminutive enterprises that lack extensive administrative resources. Moreover, initiating a modest enterprise in nations with streamlined regulatory requisites is frequently linked with the intention to curtail maintenance expenditures. In territories with simplified fiscal administration and straightforward reporting protocols, entrepreneurs can attenuate expenses related to accounting assistance, legal counsel, and the like.
Registering a business in a reputable jurisdiction will bolster the assurance of financiers and collaborators. Jurisdictions with well-entrenched legal frameworks and lucid commercial practices forge a favorable visage for the enterprises established therein. Territories with elevated degrees of legal safeguarding, robust anti-corruption mechanisms, and efficacious contract adjudication allure investors, as they proffer a stable and secure milieu.
Registration of small businesses in highly developed countries gives access to highly qualified personnel. Developed economies are often driven by advanced educational systems. Such countries provide businesses with access to a variety of educational programs, advanced training courses and professional training, which is directly related to the development of in-demand skills among specialists.
Incubators, accelerators, technopoles, and research establishments unveil avenues for vocational advancement. For instance, locales such as Silicon Valley in the US are the abode of pioneering technology ventures, fostering a dynamic milieu for the interchange of erudition and avant-garde concepts.
Incubators furnish nascent enterprises with primordial assistance, including workstations, conference chambers, and ancillary apparatuses without necessitating the deployment of internal assets, guidance, and counsel, access to funding via venture capitalists, benefactors, or exclusive capital, and opportunities for networking.
Accelerators furnish more vigorous and methodical aid. They generally proffer rigorous tutelage, guidance, and entrée to assets for a finite duration, initial capital infusion in return for a stake in the enterprise, access to prominent corporate allies and clientele through gatherings, and bespoke counsel in commerce, technology, and promotion.
Technology enclaves emphasize engendering milieus conducive to the advancement of avant-garde technologies. Enlistment of nascent enterprises in foreign jurisdictions with an elaborate web of technology enclaves will afford access to cutting-edge apparatus and laboratories, premium administrative services, and backing in the monetization of innovations. Research institutions frequently engage with commercial entities to assimilate novel technologies into economic operations. They may proffer instructional programs and tutelage to cultivate adept specialists.
Access to eminently adept personnel augments the competitiveness of diminutive enterprises. Exceptionally skilled employees can facilitate innovation, refinement of business processes, and overall operational efficacy. This, in turn, aids in bolstering the standing of small enterprises in the market and enhancing their lucrativeness.
If you are intrigued by commencing your enterprise from the ground up, then you should be cognizant that in advanced nations, there is vigorous endorsement for nascent ventures and entrepreneurial endeavors. Public schemes, subsidies, and fiscal concessions assist fledgling innovators in enlisting premier experts and actualizing their avant-garde concepts.
Another boon derived from inaugurating a modest enterprise overseas is the capacity to employ adaptable global expansion stratagems. Operating in a transnational milieu fosters the establishment of networks of contacts that may prove advantageous for the augmentation of your enterprise. Commencing a venture abroad permits entrepreneurs to utilize pliant approaches such as franchising and licensing, which entails harnessing local assets and acumen for swift market ingress, or engaging in collaboration with indigenous firms, thereby facilitating adaptation to cultural and market peculiarities.
Startups and microenterprises furnish a pivotal contribution to economic advancement and innovative dynamics. These ventures bolster employment, augment human capital, thereby directly impacting the enhancement of life’s standard. In reaction to these advantages, authorities and the private sector are instituting various supportive interventions to aid these establishments in surmounting preliminary challenges and expanding.
Optimal Nations for Operating a Modest Enterprise may institute grant schemes, for instance, the American Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program proffers financing to diminutive enterprises advancing pioneering technologies. Auxiliary measures encompass loans and venture capital, incubatory networks that assist nascent ventures in evolving through the provision of workspace, guidance, and access to co-working environments and offices. The registration of a modest enterprise overseas can evolve into a potent instrument for augmenting competitiveness, enhancing fiscal performance, and mitigating perils.
How to start your business from scratch?
In establishing and managing a diminutive enterprise overseas, it is imperative to formulate a tactical approach that considers the distinctive juridical and regulatory circumstances of the intended nation. In this regard, acclimatization to and comprehension of regional statutes and the idiosyncrasies of the commercial milieu will not merely guarantee adherence to all edicts but also streamline procedures for optimal business efficacy.
A synopsis of the principal stages you must undertake to commence a modest enterprise overseas:
- Formulating a business scheme that delineates the enterprise's mission, vision, and strategic objectives, initial capital infusion, operational expenditures, and anticipated revenues.
- Selecting a jurisdiction for instituting a modest enterprise.
- Ascertainment of the most advantageous juridical structure.
- Authentication and ratification of the distinctive trade appellation.
- Compilation, enactment, and presentation of a comprehensive dossier.
- Securing permits, if necessary.
- Commencing an account for a modest enterprise, it is paramount to juxtapose the stipulations and rates of various establishments, which will assist you in arriving at a well-considered judgment.
Consultations and comprehensive assistance in the procedure of establishing a modest enterprise will aid in streamlining the process.
Selecting a juridical configuration for diminutive enterprises
This is a primordial determination that influences juridical and pecuniary duties, the fiscal apparatus, and administrative methodologies. The precise selection of OPF can ameliorate expenditures and levies, enhance corporate governance, and mitigate perils. Attributes of the principal configurations are enumerated below.
|
Individual entrepreneur |
Joint stock company |
Limited Liability Company |
Partnership |
|
|
Advantages |
Facilitation of genesis and stewardship. Minimizing expenditures for bookkeeping and fiscal services. All decisions are made solely by the owner. |
The owner risks only the capital invested in the company. |
Ease of organization. |
|
|
Possibility of raising capital through the issue of shares. |
Flexibility in strategic management and income distribution. |
|||
|
Possibility of attracting investors through the sale of shares. |
||||
|
Flaws |
The owner is liable for the debts of the business with his personal property. Limited opportunities for attracting investment. |
Labor-intensive and financially burdensome procedures for preparing and maintaining reporting documentation. The obligation to disclose financial information and comply with strict corporate regulations may incur significant legal and financial costs. |
A more complex registration and reporting procedure compared to individual entrepreneurs. There are limitations on the quantity of contributors. |
Partners are jointly and severally liable for the company's debts. Limited opportunities to attract external investment. |
For disparate modalities in which you may inaugurate a diminutive enterprise, distinguished by varied fiscal encumbrances. For instance, a streamlined tax regimen is enforced upon sole proprietors, whereas Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) and Joint Stock Companies (JSCs) are mandated to uphold more intricate bookkeeping and proffer disclosures.
Standards by which you might select a nation for modest enterprise
Selecting the most advantageous jurisdiction for establishing a modest enterprise necessitates a thorough appraisal of various considerations. Primarily, one should assess the fiscal advantages impacting the company’s economic outcomes. It is imperative to factor in the convenience of operating and expenditures. Equally critical is the availability of market prospects that may unveil avenues for expansion. The juridical transparency of a jurisdiction is pivotal in safeguarding the dependability and enduring prosperity of an enterprise. Business proprietors frequently consult global rankings to identify the most appropriate jurisdictions for setting up a small business.
The Conducting Commerce rating is one of the most renowned indices that appraises the facility of establishing and managing a business by nation. The hierarchy encompasses several pivotal aspects, including:
- Duration and expenditure of instituting a nascent enterprise.
- Protocols for procuring edifice and ancillary licenses.
- Fiscal encumbrance.
- Entry to credit and funding.
- Terms for export-import transactions.
- The efficacy of the judicial apparatus in adjudicating commercial conflicts.
- Legal safeguarding of the entitlements of stockholders and financiers.
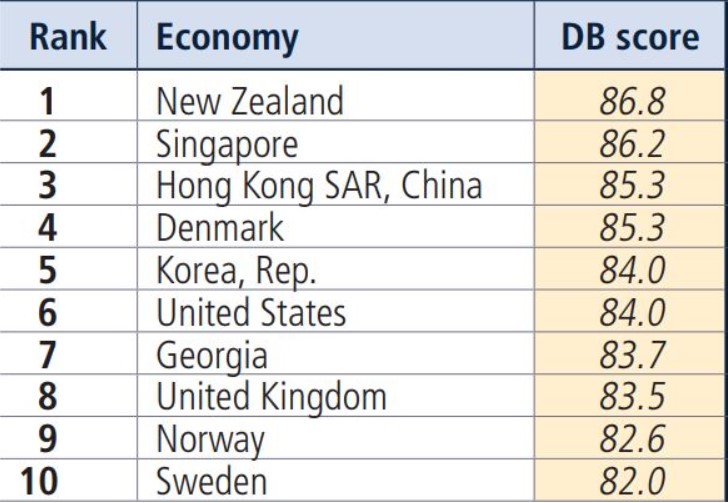
Top 10 Doing Business 2020 rating.
The Global Competitiveness Index (GCI) assesses the rivalry of nations predicated on variables such as infrastructure, macroeconomic steadiness, pedagogy, healthcare, innovation, and commercial milieu. This appraisal aids in discerning the extent to which the nation's authorities bolster entrepreneurship.
The top GCI countries included Singapore, Hong Kong, UAE.
The EIU's Facility of Commerce Assessment emphasizes the commercial milieu and the extent of regulation. It appraises business reforms, the intricacy of fiscal administration, the degree of malfeasance, and other determinants that influence enterprising endeavors.
The Forbes Optimal Territories for Commerce enumeration considers a plethora of determinants, such as fiscal statutes, workforce composition, prevalence of malfeasance, avenues to capital, and various other pivotal components of the mercantile milieu. The index facilitates the evaluation of which nations present the most allure for engaging in commerce from the perspective of external financiers. In this appraisal, Hong Kong ascended into the triad of leaders with an economic expansion of 3.8%, a gross domestic product per inhabitant of 46,200 American denominations, and a trade surplus of 4.3%.
The Innovation Index appraises the magnitude of ingenuity and bolsters enterprisers and minor firms that pioneer novelties and apparatuses. This tabulation (the ledger beneath exhibits the foremost 10 nations) scrutinizes elements that facilitate inventiveness, such as frameworks, inquiry and advancement, endowment in machinery and imaginative sectors.
|
Position in the ranking |
Side |
2024 |
2023 |
2022 |
|
1 |
Switzerland |
67.6 |
67.6 |
65.5 |
|
2 |
Sweden |
64.2 |
64.2 |
63.7 |
|
3 |
United States |
63.5 |
63.5 |
61.3 |
|
4 |
Great Britain |
62.4 |
62.4 |
61.7 |
|
5 |
Singapore |
61.5 |
61.5 |
59.2 |
|
6 |
Republic of Korea |
61.2 |
61.2 |
59.9 |
|
7 |
The Netherlands |
60.4 |
60.4 |
59.8 |
|
8 |
Germany |
59.6 |
59.6 |
58.9 |
|
9 |
Finland |
59.5 |
59.5 |
58.1 |
|
10 |
Denmark |
59.4 |
59.4 |
58.6 |
Rating of the best countries for running a small business
Among best countries to register a small business, both according to rating indicators and taking into account other features, for example, tax preferences - Singapore, Hong Kong, USA, Portugal, Georgia.
Inaugurating a diminutive enterprise in Singapore
Singapore is deemed among the globe's preeminent fiscal and commercial hubs, offering auspicious vistas for enlisting and steering a modest enterprise. Its renown among enterprisers is attributed to myriad elements, encompassing a steadfast economy, propitious taxation protocols, and avant-garde mercantile frameworks.
Singapore is delineated as one of the most cutthroat and unbarred marketplaces globally, boasting a pellucid judicial framework and negligible degrees of venality. The business enrollment procedure in Singapore is swift and effectual. Via the Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA) conduit, one can enlist a Singaporean enterprise digitally within a solitary diurnal span.
The nation boasts entrenched conveyance and telecommunication grids, while top-tier fiscal and juridical amenities are obtainable. The existence of a copious quantity of enterprise nurseries and hastening schemes affords assistance to nascent ventures at variegated phases of maturation.
Owing to its propitious placement in Southeastern Asia, Singapore functions as an entrée to mercantile arenas in the Asia-Pacific expanse. The nation possesses copious pacts for commerce, facilitating the movement of exports and imports. Singapore upholds an elevated echelon of safeguarding for proprietors’ entitlements and their holdings. Administrators bolster technological fledglings by proffering stipends and endowments to buttress investigational endeavors.
When selecting, where is the optimal locus to establish a venture to operate a diminutive enterprise internationally in 2026, it is prudent to scrutinize the preliminary expenditures. Establishing a modest enterprise in Singapore proves advantageous, as the inception capital for limited liability entities is stipulated at 1 SGD. Permitting operations through a digital office emerges as a boon for petite enterprises, given that leasing a physical office may substantially augment outlays.
After minute enterprise registration in Singapore, a clerk must be designated within six months; the fee for services fluctuates between 300 to 1 thousand SGD yearly, contingent upon the extent of services rendered. Although diminutive firms that satisfy specific criteria are absolved from yearly examinations, bookkeeping services in Singapore persists as obligatory. This service expenses between SGD 500 to 2 thousand annually and encompasses preserving financial ledgers, drafting statements, and adhering to all statutory stipulations.
Minute enterprise registration in Hong Kong
Hong Kong, an eminent financial nexus globally, rightfully secures a premier position on the roster of nations for instituting a modest enterprise. This dominion presents a propitious milieu for nascent ventures and diminutive enterprises owing to its strategic situs, streamlined registration and bureaucratic protocols, and an extensive array of pecuniary services.
Hong Kong is acknowledged as one of the most advantageous locales for commercial endeavors due to its permissive fiscal regulations and unrestricted marketplace. There are no monetary constraints, facilitating fiscal dealings and transnational investments with greater ease.
The enterprise registration procedure in Hong Kong is relatively uncomplicated and efficacious. Establishing a corporation necessitates a scant quantity of paperwork and temporal investment. Enrollment can be finalized in merely a few days via e-Registry. All juridical and commercial documentation can be presented in English, facilitating the process for non-native investors to engage in trade.
Hong Kong is renowned for its exquisitely cultivated pecuniary apparatus. Its geomorphological positioning renders it a significant mercantile nexus betwixt the Orient and Occident. Superior-grade workspaces and commercial precincts proffer felicitous circumstances for conducting commerce.
The enrollment levy hinges on the category of corporation. For instance, for Ltd registration in Hong Kong, the charge is 1,720 HKD. A phantom office is permissible and can substantially diminish initiation expenses. Office charges may fluctuate from 1 thousand to 4 thousand HKD per month. Establish a corporation in Hong Kong feasible with a token capital of merely 1 HKD. Generally, streamlined fiscal stipulations pertain to petite enterprises.
Registering a small business in the USA
The US has the largest economy in the world with highly developed sectors such as finance, technology, healthcare and consumer goods. This creates ample business opportunities and guarantees a stable market. The country is known for its innovative culture and strong support for startups. Silicon Valley, Silicon Valley and other technology hubs provide startups in the USA access to capital, mentors and a network of professionals.
USA have one of the strictest systems protection of intellectual assets, which is important for innovative companies. Patents, trademarks and copyrights are protected at the federal level. The United States has a highly developed transportation, communications and technology infrastructure, which facilitates efficient logistics and customer interactions, access to a large domestic market, as well as international markets through a variety of trade agreements and treaties.
The country's labor laws provide flexibility regarding the hiring and firing of employees. There are many financial grant programs, counseling services and training programs available. There are various associations and networks in the United States that support entrepreneurs and small businesses through access to resources and networking opportunities.
Business registration process in the USA may take from several days to several weeks. Company registration in the USA requires payment of a state fee, the amount of which depends on the state and type of company, and can range from 50 to 500 USD for an LLC, while for a C-Corp this amount ranges from 100 to 800 USD.
To form a company in most US states, you need a registered agent with a physical location in a specific state. A corporate secretary is not always required by law, but appointing one simplifies organizational processes. Costs for corporate secretary services vary from 500 to 2 thousand USD monthly.
Registering a small business in Portugal
Portugal provides entrepreneurs with a stable and supportive business environment. Portugal is located at the crossroads of trade routes between Europe, Africa and America. This makes the country a strategically important hub for international trade and business. The Portuguese ports of Lisbon and Porto provide excellent logistics capabilities for the export and import of goods.
In recent years, the country has adopted a number of reforms aimed at simplifying procedures for business, including simplifying company registration and reducing bureaucratic barriers. Company registration in Portugal takes little time and can be done through a digital platform or in one of the One Stop Shops (Balcão Único de Empresa). The online registration fee is approximately 360 EUR.
In Portugal, a virtual office can be used to manage a company (the cost of services can be obtained from professionals). As for other costs registration of a small business in Portugal, then for Lda it is necessary to deposit an initial capital of 5 thousand EUR, while for S.A. the initial capital is set at 50 thousand EUR.
The government supports startups through special programs and funds. For example, the Startup Visa program offers foreign entrepreneurs the opportunity get a visa through starting a business in Portugal, access to funding and mentoring support.
Registration of small business in Georgia
A stable political situation is maintained in Georgia. The economy is showing positive dynamics with steady growth in a wide range of sectors. Georgia known for its efficient business registration system, which makes company creation process fast. There is a possibility register a business in Georgia online through the Georgian Business Portal platform.
Cost of registering a company in Georgia is about 38 USD. Can register a small business in Georgia with no specified minimum capital contribution obligations. The cost of a virtual office ranges from 50 to 150 USD monthly. The presence of various business incubators and acceleration programs for innovative projects, a high standard of living at relatively low costs make this country one of the most preferred options for small business registration in Europe.
Support programs for small businesses
|
Singapore |
|
|
Hong Kong |
|
|
USA |
|
|
Portugal |
|
|
Georgia |
|
The impact of tax reforms on various aspects of small business activities
Tax reforms, among other things, shape the economic environment for small businesses. These changes may significantly affect financial results and operating activities. Reducing the tax burden allows firms to free up financial resources for reinvestment. Reducing income taxes or providing tax holidays has a direct impact on improving the financial stability of companies, especially in the first years of their existence.
Reforms aimed at reducing payroll and social security taxes encourage small business in foreign jurisdictions hire more employees. This helps reduce unemployment and increase employment in the regions. When taxes on reinvested earnings are reduced, small businesses are able to devote greater amounts of money to research and development, which leads to the creation of new products and solutions.
Changes in depreciation rules can impact the financial performance of small businesses. More flexible depreciation rules can make it easier to write off acquisition costs for long-lived assets, reducing your tax burden and improving cash flow.
In the States, according to the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), corporate tax was reduced from 35% to 21%. The TCJA introduced new tax credits and deductions, such as the 20% passive income tax credit for small businesses. The US Federal R&D Tax Credit can reduce the tax burden for businesses engaged in innovation. State tax rates range from 0% to 11.5%, and local tax levies must be added to these rates.
Singapore offers one of the most attractive tax systems:
- For business conglomerates, the corporate levy (CIT) is 17%, yet there are inducements for diminutive enterprises. Throughout the initial triennium of fiscal assessment, modest firms can avail themselves of tax alleviations that diminish the tax foundation by 75% for the inaugural 10 thousand SGD of earnings and 50% for the subsequent 190 thousand SGD.
- There is no impost on pecuniary returns, which signifies that gains allocated to stakeholders are not liable to supplementary impost. Nevertheless, you should be cognizant that the proprietorship of equities in an alien corporation by a Singapore entity that acquires pecuniary returns may culminate in the disbursement of impost on the pecuniary returns in the jurisdiction where the pecuniary returns were disbursed.
Significant factor of attractiveness Hong Kong for small business creation is its tax system. Income tax is 8.25% on the first HKD 2 million and 16.5% on amounts above this threshold. On receipts from abroad (as company profits) tax is 0%. Hong Kong is among a limited list of countries that do not pay tax on dividends, allowing business owners to receive income without additional tax costs.
Taxes in Portugal are among the most competitive in Europe, which makes it attractive for small business registration:
- Corporate tax in the main territory of the country is 21%. Small companies whose annual profits do not exceed 25 thousand euros can count on a preferential rate of 17%. Madeira company registration will allow you to pay reduced rates - 14.7% and 11.9% (with income up to the specified threshold).
- The basic VAT rate in Portugal is 23%, but reduced rates may apply (13% and 6%).
Georgia offers attractive tax conditions. Corporate tax here is 15%, and dividend tax is only 5%. There are special tax regimes for SMEs, for businesses in certain industries, such as IT and tourism. In Georgia there is a Technopark where IT companies are exempt from CIT and can claim VAT deduction on certain types of goods and services.
Small companies in Georgia often register as individual entrepreneurs and pay income tax at a rate of 1% instead of the standard 20%. CIT for corporate entities is 15%. All small businesses are required to pay 18% VAT. Micro-businesses with an annual turnover below 30 thousand lari are exempt from the tax burden.
The impact of social and environmental responsibility on choosing a country for small business
In today's world, where business and society are interconnected, social and environmental responsibility are recognized as important factors in choosing a country to open a small business. Social responsibility of business implies the company's obligations to society, including supporting local communities, respecting workers' rights, fair business practices and contribution to the development of social infrastructure.
Environmental responsibility is about minimizing the impact of a business on the environment. This may include carbon footprint reduction, waste reduction and other practices aimed at protecting ecosystems. Many countries offer incentives for companies that engage in social responsibility. These could be tax breaks, subsidies or support for corporate social responsibility (CSR) programs.
Countries with high social standards can offer businesses a competitive advantage. Companies operating in such jurisdictions can gain access to customers who value ethical principles and social responsibility, which can strengthen their brand and increase their customer base. In some states, social responsibility is a prerequisite for business projects. This may include investing in local projects or adhering to certain social standards, which can affect the company's reputation and relationships with local authorities.
Opting for a dominion to inaugurate a modest enterprise, one ought to heed which commonwealths have cultivated pecuniary and levy enticements for establishments engaging in eco-conscious undertakings. This is particularly crucial for diminutive ventures seeking to curtail expenditures whilst exemplifying their allegiance to perpetuity.
Environmental responsibility can also have an impact on attracting customers. Today, consumers are becoming increasingly aware and sensitive to environmental issues, leading to increased interest in products and services from companies actively working to protect the environment. Businesses operating in countries with progressive environmental policies may find more favorable market conditions and consumer support.
Upon resolving to inaugurate a modest enterprise in Singapore, it proves advantageous to grasp that the nation's administration is fostering the notion of enduring advancement via undertakings like Singapore 2030 and the Verdant Stratagem 2030, which accentuate ecological and communal accountability. Numerous entities and benefactions within this dominion furnish endowments for ventures that tackle societal and environmental quandaries, exemplified by the Commonwealth Social Enterprise Treasury.
If you aspire to inaugurate a modest enterprise in Hong Kong, you may procure assistance from entities such as the Hong Kong Collective Societal Accountability Consortium (HKCSRC) and the Hong Kong Coalition for Enduring Advancement (HKSD). The HKCSRC orchestrates symposiums, tutelage, and advisories for corporations to aid them in embedding ethical responsibility doctrines into their commerce frameworks. HKSD facilitates enterprises in devising and actualizing perpetuity blueprints, encompassing asset stewardship, communal ramifications, and corporate oversight.
Certain entities, like Enterprise for Societal Accountability (ESA), diligently assist major corporations and modest enterprises in the United States in the formulation and execution of societal duty blueprints. The nation enacted the Corporate Societal Obligation (CSO) Revelation Statute, mandating organizations to divulge particulars regarding their ecological, ethical, and societal endeavors.
Talking about Portugal as a jurisdiction for small businesses, it will be useful to know that the Sustainability Reporting Program (Relatório de Sustentabilidade) was launched here. Many companies are required to publish annual reports on their sustainability and CSR achievements. This increases transparency and promotes a better understanding of the social impact of a business.
CSR is developing in Georgia, although on a more limited scale compared to Portugal. The CSR program within the framework of the Georgian Chamber of Commerce and Industry supports companies in the development and implementation of CSR strategies, seminars and trainings are held on CSR practices. The Georgian Business and Ecology Association helps companies integrate environmental and social standards into their business practices, supporting sustainable development initiatives. Generally, CSR initiatives help strengthen the image of companies, attract investment and create competitive advantages.
Conclusion
The modern economic environment, characterized by rapid technological changes and dynamism, poses small business the task of quickly responding to changes and strategically approaching choosing a jurisdiction for registration. Small business owners need to consider both internal conditions and external factors, including sustainability and social responsibilities, to ensure competitiveness.
The TK Deal team can provide expert advice and help determine the most suitable jurisdiction for small businesses, drawing on our experience in international corporate law.




 How to get a banking license
How to get a banking license  Obtaining a cryptocurrency licence
Obtaining a cryptocurrency licence  Navigating cryptocurrency exchange registration in 2026
Navigating cryptocurrency exchange registration in 2026  EMI licensing
EMI licensing  Countries with no dividend tax
Countries with no dividend tax  Choice of jurisdiction for registration of an IT company
Choice of jurisdiction for registration of an IT company  Top countries to open a company in Asia in 2026
Top countries to open a company in Asia in 2026  Launch of a crowdlending platform
Launch of a crowdlending platform  Crypto business software solution
Crypto business software solution